Puede que sea totalmente incorrecto por poner este Instructables pero he luchado para encontrar una manera fácil de corregir datos de fecha y hora de GPS a mi zona horaria aquí en Australia. He realizado algunos proyectos de Arduino que han incluido un módulo de GPS con algún tipo de registro de datos. Cada vez han tenido dificultades convertir hora UTC capturado de la cadena de datos NMEA a hora local o tienen simplemente para arriba y un RTC en mi proyecto.
Hay que algunas soluciones en la web incluyen un par aquí en Instructables, pero como un programador aficionado he luchado para integrar el código en mis propios bosquejos.
Esperemos que esta publicación le dará los igualmente luchando, una solución fácil. He tratado de mantener el código tan simple como sea posible con un montón de opciones para sus conexiones seriales de instalación, Uno o Mega, software y hardware. También he puesto el cálculo de la zona horaria en una función simple que se puede copiar y pegar directamente en su propio dibujo.
Usted necesitará instalar la TinyGPS ++ Library y la Biblioteca de AltSoftSerial para el bosquejo para compilar correctamente. He tenido mejor compatibilidad con los módulos GPS que tengo usando la biblioteca TinyGPS ++. La biblioteca de AltSoftSerial hace más fácil tener múltiples dispositivo serie conectado a tu Uno. Esto no es un problema cuando se utiliza un Mega pero si usted quiere conectar dispositivos serie en pines digitales diferentes, esta es la biblioteca más fácil que he encontrado.
Aquí está el bosquejo siguiente:
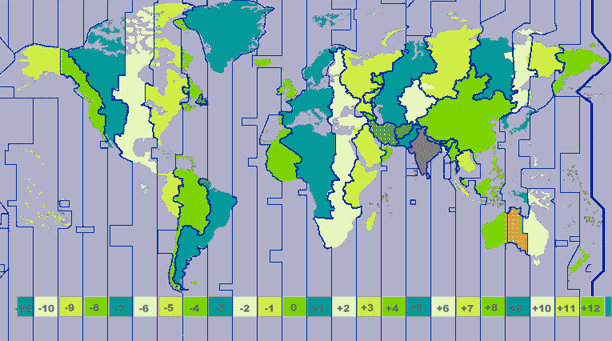
#include <Time.h> // Time Library #include <TinyGPS++.h> // GPS Library #include <AltSoftSerial.h> // Allows two Serial connections // Set GPS RX and TX pins if using software serial connections. // See below to use hardware serial connections //static const int RXPin = 4, TXPin = 3; // Example Uno static const int RXPin = 48, TXPin = 46; // Example Mega static const uint32_t GPSBaud = 4800; //static const uint32_t GPSBaud = 9600; // The TinyGPS++ object TinyGPSPlus gps; // Serial connection to the GPS device AltSoftSerial Serial_GPS; //#define Serial_GPS Serial1 // Uncomment this line & comment // above line to use a hardware // Serial Port // Change this value to suit your Time Zone const int UTC_offset = 10; // Eastern Australia Time time_t prevDisplay = 0; // Count for when time last displayed void setup() { Serial.begin(9600); Serial_GPS.begin(GPSBaud); // Start GPS Serial Connection Serial.println("Waiting for GPS time ... "); } void loop() { GPS_Timezone_Adjust(); // Call Time Adjust Function } void GPS_Timezone_Adjust(){ while (Serial_GPS.available()) { if (gps.encode(Serial_GPS.read())) { int Year = gps.date.year(); byte Month = gps.date.month(); byte Day = gps.date.day(); byte Hour = gps.time.hour(); byte Minute = gps.time.minute(); byte Second = gps.time.second(); // Set Time from GPS data string setTime(Hour, Minute, Second, Day, Month, Year); // Calc current Time Zone time by offset value adjustTime(UTC_offset * SECS_PER_HOUR); } } // -- Delete this section if not displaying time ------- // if (timeStatus()!= timeNotSet) { if (now() != prevDisplay) { prevDisplay = now(); SerialClockDisplay(); } } // -- Also delete the SerialClockDisplay()function ---- // } // Keep void SerialClockDisplay(){ // Serial Monitor display of new calculated time - // once adjusted GPS time stored in now() Time Library // calculations or displays can be made. if (hour() < 10) Serial.print(F("0")); Serial.print(hour()); Serial.print(F(":")); if (minute() < 10) Serial.print(F("0")); Serial.print(minute()); Serial.print(F(":")); if (second() < 10) Serial.print(F("0")); Serial.print(second()); Serial.print(" "); if (day() < 10) Serial.print(F("0")); Serial.print(day()); Serial.print(F("/")); if (month() < 10) Serial.print(F("0")); Serial.print(month()); Serial.print(F("/")); Serial.println(year()); } Espero que haya encontrado este útil y hace que su próximo proyecto de registro de datos GPS mucho más fácil.