Paso 4: Recibir Arduino: el código.
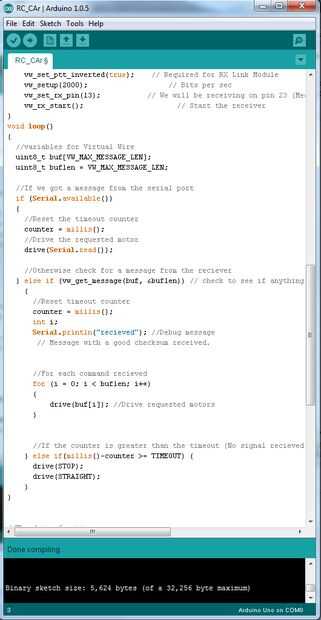
#include <VirtualWire.h> //Include required library
También vamos a definir algunas constantes que vamos a utilizar para controlar nuestra coche:
#define FORWARD '8' #define BACKWARD '5' #define STOP '0' #define LEFT '4' #define RIGHT '6' #define STRAIGHT '/' #define TIMEOUT 500UL
Luego viene las variables para los pernos de motor. El valor de estas variables será cualquier pin del cable está conectado en el Arduino. Si usted había cableado suyo diferentemente Asegúrese de que actualizar su código aquí:
int motor1Pin1 = 5; // pin 2 on L293D is connected to this pin on the Arduino int motor1Pin2 = 6; // pin 7 on L293D " int enablePin1 = 9; // pin 1 on L293D " int motor2Pin1 = 3; // pin 10 on L293D "int motor2Pin2 = 4; // pin 15 on L293D " int enablePin2 = 10; // pin 9 on L293D "
Hay dos variables para controlar las velocidades del motor:
int motor1Speed = 255; //max speed 255 int motor2Speed = 255;
La última variable es para el contador de tiempo de espera:
unsigned long counter;
La función de configuración establecerá los pernos según se requiera. También fijó de arriba alambre Virtual:
void setup() { //Set pin modes pinMode(motor1Pin1, OUTPUT); pinMode(motor1Pin2, OUTPUT); pinMode(motor2Pin1, OUTPUT); pinMode(motor2Pin2, OUTPUT); pinMode(enablePin1, OUTPUT); pinMode(enablePin2, OUTPUT); //Set enablePin to the motors speed analogWrite(enablePin1, motor1Speed); analogWrite(enablePin2, motor2Speed); //Begin with motors off digitalWrite(motor1Pin1, LOW); digitalWrite(motor1Pin2, LOW); digitalWrite(motor2Pin1, LOW); digitalWrite(motor2Pin2, LOW); Serial.begin(9600); //Initialise the IO and ISR vw_set_ptt_inverted(true); // Required for RX Link Module vw_setup(2000); // Bits per sec vw_set_rx_pin(13); // We will be receiving on pin 23 (Mega) ie the RX pin from the module connects to this pin. vw_rx_start(); // Start the receiver } La función de bucle contendrá el siguiente código:
void loop() { //variables for Virtual Wire uint8_t buf[VW_MAX_MESSAGE_LEN]; uint8_t buflen = VW_MAX_MESSAGE_LEN; //If we got a message from the serial port if (Serial.available()) { //Reset the timeout counter counter = millis(); //Drive the requested motor drive(Serial.read()); //Otherwise check for a message from the reciever } else if (vw_get_message(buf, &buflen)) // check to see if anything has been received { //Reset timeout counter counter = millis(); int i; Serial.println("recieved"); //Debug message // Message with a good checksum received. //For each command recieved for (i = 0; i < buflen; i++) { drive(buf[i]); //Drive requested motors } //If the counter is greater than the timeout (No signal recieved) then stop the car. } else if(millis()-counter >= TIMEOUT) { drive(STOP); drive(STRAIGHT); } } Por último debemos definir la función Drive():
void drive(int dir) { //Check which direction is requested (same for below) if (dir == FORWARD) { Serial.println("Forward");//Used for debugging //Set motor accordingly (same for below) digitalWrite(motor1Pin1, HIGH); digitalWrite(motor1Pin2, LOW); } else if (dir == BACKWARD) { Serial.println("Backward"); digitalWrite(motor1Pin1, LOW); digitalWrite(motor1Pin2, HIGH); } else if (dir == STOP) { Serial.println("Stop"); digitalWrite(motor1Pin1, LOW); digitalWrite(motor1Pin2, LOW); } else if(dir == STRAIGHT) { Serial.println("Straight"); digitalWrite(motor2Pin1, LOW); digitalWrite(motor2Pin2, LOW); }else if (dir == LEFT) { Serial.println("Left"); digitalWrite(motor2Pin1, LOW); digitalWrite(motor2Pin2, HIGH); }else if (dir == RIGHT) { Serial.println("Right"); digitalWrite(motor2Pin1, HIGH); digitalWrite(motor2Pin2, LOW); } } Puede descargar el bosquejo completo desde aquí: https://dl.dropboxusercontent.com/u/63127140/RC_CA...