Paso 4: mando a distancia

Como se define:
#define UNIFIEDFUNCTION "theFunction"
y luego en setup():
Spark.function(UNIFIEDFUNCTION, setColorInModeFunction);
Esta función de llamada de Internet a través del NSURLRequest luego sucursales en varias partes según el modo y los valores de la cuenta. Esta parte puede conseguir quizá más sofisticada, y así sucesivamente se podría introducir una suma de comprobación.
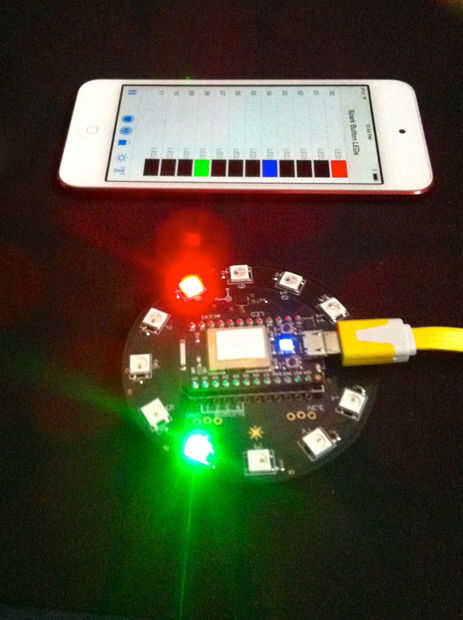
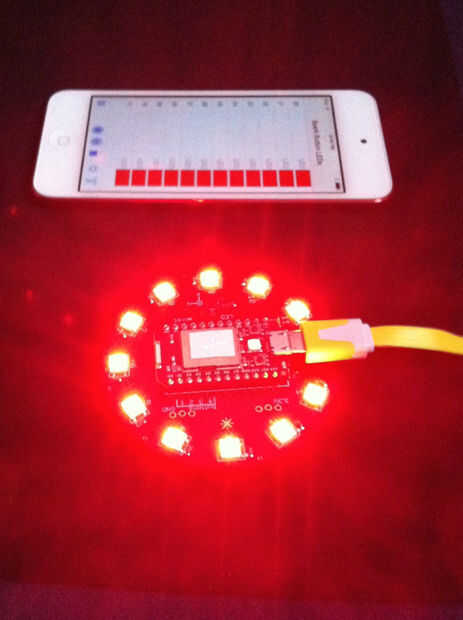
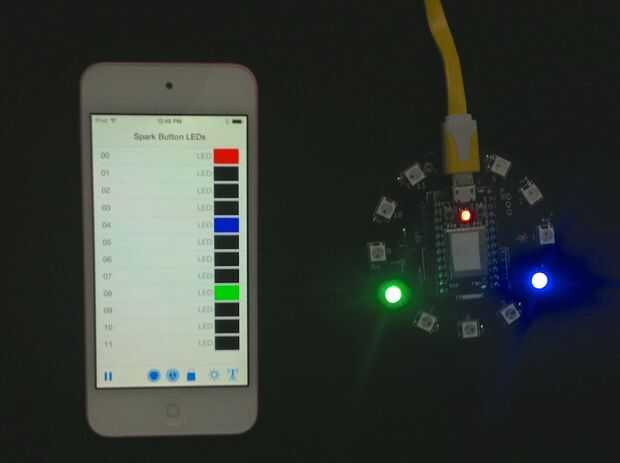
int setColorInModeFunction(String args) { unsigned char allValuesMaxCount = 25; // 64 chars -24 separator = 40 digis; // 40/25 digits = 1.6 digits per value double allValues[allValuesMaxCount]; unsigned int count = parseArgsIntoDoubles(args, allValues); if(count > allValuesMaxCount) {// How to deal with a once-in-a-lifetime situation? Serial.println("Houston, we have a problem!"); } double mode = allValues[0]; if(THEFEATURE_FUNCTION == mode)// set overall brightness and rotation {// 1 == rpm, 2 = brightness double rotationExponent = allValues[1]; rotationDirectionIsClock = (0 < rotationExponent); float buttonRpmExp = (float)fabs(rotationExponent); rpm = (unsigned int) round(pow(2,buttonRpmExp));// the only case we get fractional exponents, e.g. smooth changes buttonRpmIndex = (unsigned char)round(buttonRpmExp);// to get the buttons as index right brightness = (float)constrain(allValues[2],0.0,1.0); int exp; double fraction = frexp(256.0*brightness, &exp); brightnessIndex = (unsigned char)constrain(exp,0,7); } else if (SINGLECOL_FUNCTION == mode && 3 == count)// set one indexed color { unsigned int aColorIndex = constrain((unsigned long)(floor(allValues[1])),0,11); theColorValues[aColorIndex] = constrain((unsigned long)(floor(allValues[2])),0,0xFFFFFF); } else // some more or all colors will be set { unsigned char startIndex = 0; unsigned char offset = 0; unsigned char colorsCount = 12; // 12: there will be 12 values for all the LEDs, there is no mode, value is positive if( 0 <= mode && 12 == count)// we got all values, no explicit mode { // nothing } else if(INDEXEDCOL_FUNCTION == mode) { // set all values for the loop startIndex = constrain((unsigned long)(floor(allValues[1])),0,11); colorsCount = constrain((unsigned long)(floor(allValues[2])),1,12); offset = 3; } if(13 > startIndex + colorsCount)// no more than 12 for(unsigned int i = 0; i < colorsCount ; i++) {// set the indexed color from offset to end unsigned char readIndex = offset + i; // for readability, start at offset; theColorValues[i + startIndex] = constrain((unsigned long)(floor(allValues[readIndex])),0,0xFFFFFF); }; } return count; } Las imágenes muestran algunos casos especiales. Los LED en rojo acorta la llamada, porque el color rojo es 0x0000FF hex, decimal sólo 256. Esto es sólo en la llamada. Las siguientes dos imágenes muestran tanto un montón de LEDs en color negro, que le da una cadena de '0'.
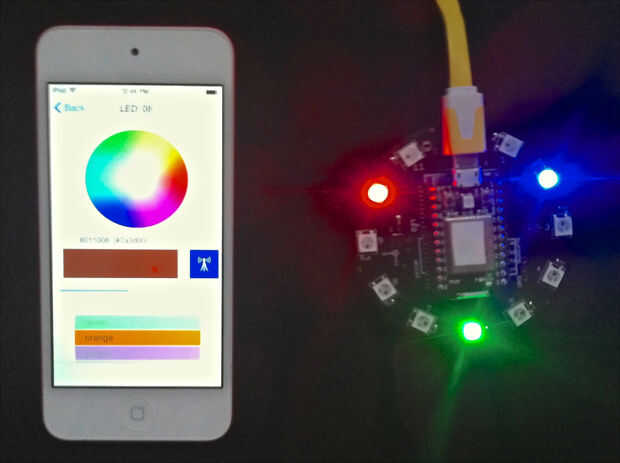
La última muestra la interfaz para definir un color con un colorwheel y un control deslizante de brillo. Desde esta interfaz el color se puede definir como color único.













