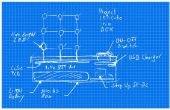
Paso 3: programación
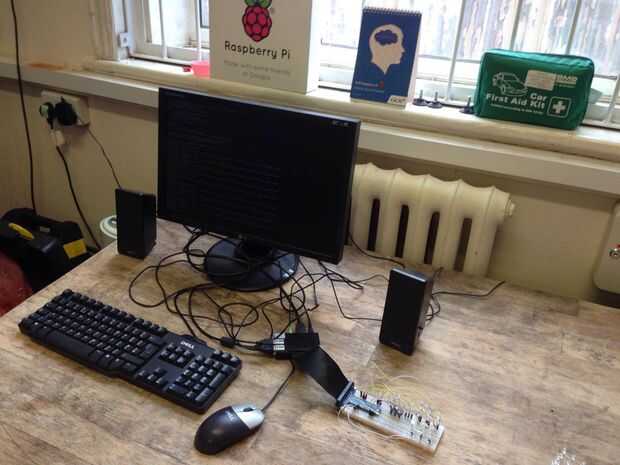

El siguiente programa Python simple muestra cómo se encienden los LEDs en bonitos los patrones:
#**************************************************************************************
#*
#* Título: 3 x 3 cubo del LED #* #* Descripción: Simple LED cubo para soldar práctica y demostrar algunos #* matriz manejo con GPIO pins #* - pines P1 a P9 se conectan al LED cátodo (-) #* - capas están conectadas al ánodo del LED (+) #* #* autor: Jacob Groves, Makerspace Coventry #* #***
importar RPi.GPIO como GPIO de importación sueño
# Assign the individual LED pins a variable name . . . P1 = 13 P2 = 19 P3 = 26 P4 = 23 P5 = 24 P6 = 25 P7 = 16 P8 = 20 P9 = 21
# Assign the layers to a nice variable . . . Top = 17 Middle = 27 Bottom = 22
# LED sequences represented by an array . . . aPins = [P1, P2, P3, P4, P5, P6, P7, P8, P9] aPinsReversed = [P9, P8, P7, P6, P5, P4, P3, P2, P1] aPinsStar = [P1, P2, P3, P6, P9, P8, P7, P4] aPinsStar2 = [P9, P8, P7, P4, P1, P2, P3, P6] aPinsSpiral = [P1, P2, P3, P6, P9, P8, P7, P4, P5] aPinsSpiralReversed = [P5, P4, P7, P8, P9, P6, P3, P2, P1]
aLayers = [Top, Middle, Bottom]
# Time delay built in between pin output . . . delay = 0.15
#************************************************************************** #* setupColumns - Initialisation of the pins . . . #************************************************************************** def setupColumns():
# GPIO pin addressing will use the virtual number . . . GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM)
# Initialise the pins so we can output values to them . . . GPIO.setup(aPins, GPIO.OUT) GPIO.setup(aLayers, GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.output(aPins, False) GPIO.output(aLayers, True) #************************************************************************** #* cyclePins - Receive array of pins & light them up one by one . . . #************************************************************************** def cyclePins(pPins):
for iPin in pPins: GPIO.output(iPin, True) sleep(delay) GPIO.output(iPin, False)
#************************************************************************** #* cyclePinsPair - Receive 2 arrays of pins & light them up in pairs . . . #************************************************************************** def cyclePinsPair(pPins, pPins2):
for iPin in range(len(pPins)): GPIO.output(pPins[iPin], True) GPIO.output(pPins2[iPin], True) sleep(delay) GPIO.output(pPins[iPin], False) GPIO.output(pPins2[iPin], False)
#************************************************************************** #* Mainline logic . . . #************************************************************************** try: print('Press CTRL+C to stop script') i = 0 while(true):
# Spinning star . . . GPIO.output(aLayers, True) GPIO.output(P5, True) cyclePinsPair(aPinsStar, aPinsStar2) cyclePinsPair(aPinsStar, aPinsStar2) GPIO.output(P5, False)
# Zig-zaggy columns . . . GPIO.output(aLayers, True) cyclePins(aPins) cyclePins(aPinsReversed) GPIO.output(aLayers, False)
# Spiral columns . . . GPIO.output(aLayers, True) cyclePins(aPinsSpiral) cyclePins(aPinsSpiralReversed) GPIO.output(aLayers, False)
# Zig-zaggy layers . . . GPIO.output(Top, True) cyclePins(aPins) GPIO.output(Top, False) GPIO.output(Middle, True) cyclePins(aPinsReversed) GPIO.output(Middle, False) GPIO.output(Bottom, True) cyclePins(aPins) GPIO.output(Bottom, False) sleep(delay) except KeyboardInterrupt: GPIO.cleanup()
finally: GPIO.cleanup()
de >