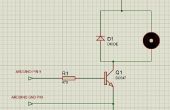
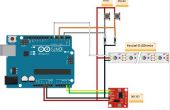
Paso 1: Poder de monitoreo usando arduino
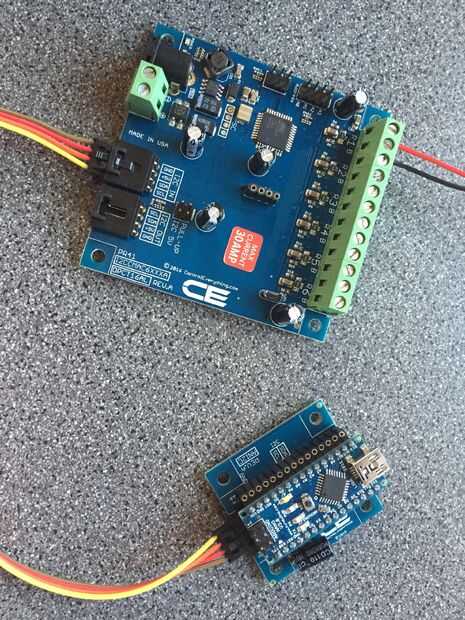
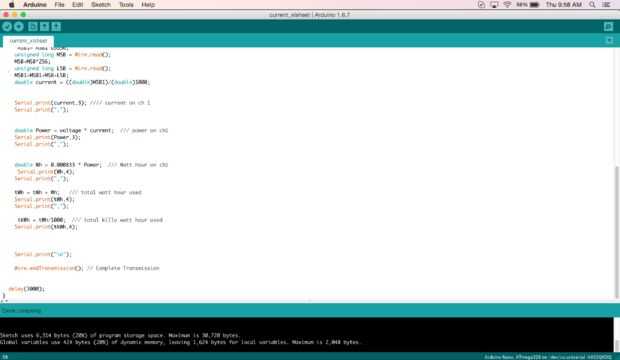
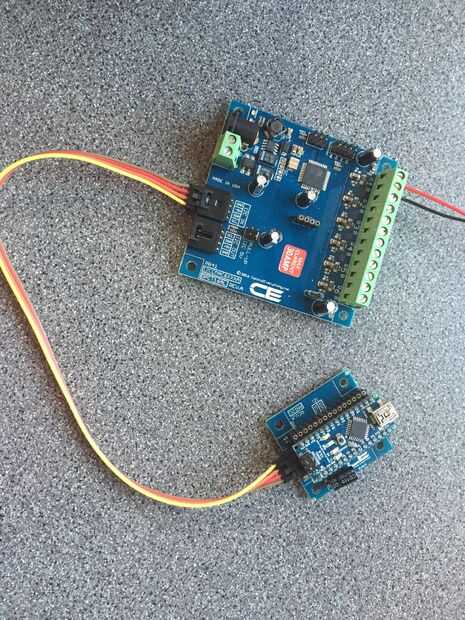



permite iniciar con el código de arduino.
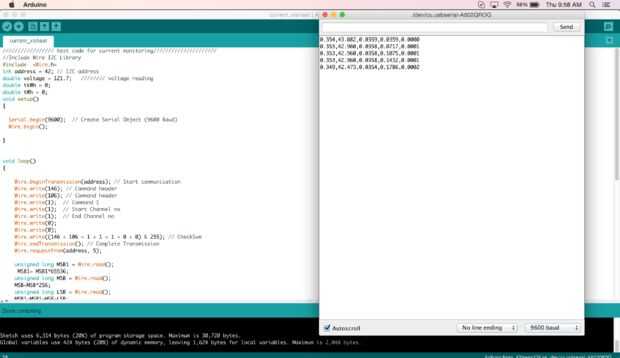
en este código, voy a escribir un comando para leer actual a través de I2C.
Este código es bastante recto hacia adelante, todo lo que necesitas hacer es enviar un comando para lectura actual y la actual Junta de vigilancia hará todo lo posible para usted.
En mi zona la CA de voltaje es alrededor de 120-124V. usaremos esta lectura de voltaje para calcular los usos de la energía.
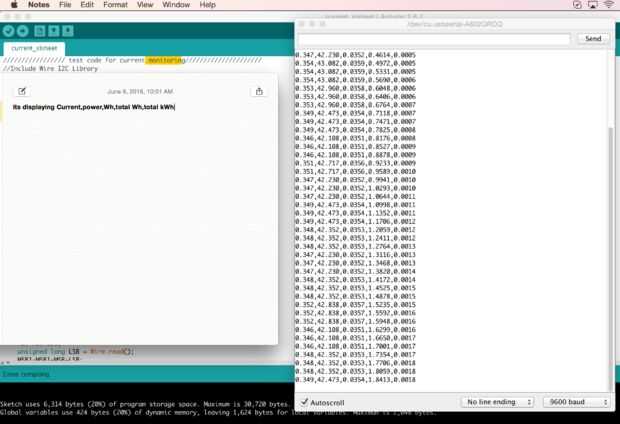
en este código am calcular corriente, potencia, vatios hora, vatio-hora total y total kilo vatio hora.
//Include Wire I2C Library #include <wire.h> int address = 42; // I2C address double voltage = 121.7; //////// voltage reading double tkWh = 0; double tWh = 0; void setup() { Serial.begin(9600); // Create Serial Object (9600 Baud) Wire.begin(); } void loop() { Wire.beginTransmission(address); // Start communication Wire.write(146); // Command header Wire.write(106); // Command header Wire.write(1); // Command 1 Wire.write(1); // Start Channel no Wire.write(1); // End Channel no Wire.write(0); Wire.write(0); Wire.write((146 + 106 + 1 + 1 + 1 + 0 + 0) & 255); // CheckSum Wire.endTransmission(); // Complete Transmission Wire.requestFrom(address, 5); unsigned long MSB1 = Wire.read(); MSB1= MSB1*65536; unsigned long MSB = Wire.read(); MSB=MSB*256; unsigned long LSB = Wire.read(); MSB1=MSB1+MSB+LSB; double current = ((double)MSB1)/(double)1000; Serial.print(current,3); //// current on ch 1 Serial.print(","); double Power = voltage * current; /// power on ch1 Serial.print(Power,3); Serial.print(","); double Wh = 0.000833 * Power; /// Watt hour on ch1 Serial.print(Wh,4); Serial.print(","); tWh = tWh + Wh; /// total watt hour used Serial.print(tWh,4); Serial.print(","); tkWh = tWh/1000; /// total kilo watt hour used Serial.print(tkWh,4); </p><p> Serial.print("\n"); Wire.endTransmission(); // Complete Transmission delay(3000); }