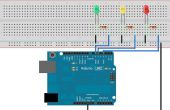
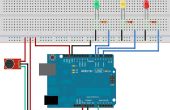
Paso 2: Cargar el código para el Arduino
Ahora tienes que subir el siguiente código a su Arduino. También puede descargar el sketch de Arduino desde el enlace en la parte inferior de la página. Antes de subir el código, correctamente debe instalar las bibliotecas de servidor BitVoicer en el IDE de Arduino (importar un .zip biblioteca).
#include <BVSP.h> #include <BVSMic.h> // Defines the Arduino pin that will be used to capture audio #define BVSM_AUDIO_INPUT 5 // Defines the LED pins #define RED_LED_PIN 6 #define YELLOW_LED_PIN 9 #define GREEN_LED_PIN 10 // Defines the constants that will be passed as parameters to // the BVSP.begin function const unsigned long STATUS_REQUEST_TIMEOUT = 1000; const unsigned long STATUS_REQUEST_INTERVAL = 2000; // Defines the size of the audio buffer const int AUDIO_BUFFER_SIZE = 64; // Defines the size of the receive buffer const int RECEIVE_BUFFER_SIZE = 2; // Initializes a new global instance of the BVSP class BVSP bvsp = BVSP(); // Initializes a new global instance of the BVSMic class BVSMic bvsm = BVSMic(); // Creates a buffer that will be used to read recorded samples // from the BVSMic class byte audioBuffer[AUDIO_BUFFER_SIZE]; // Creates a buffer that will be used to read the commands sent // from BitVoicer Server. // Byte 0 = pin number // Byte 1 = pin value byte receiveBuffer[RECEIVE_BUFFER_SIZE]; void setup() { // Sets up the pin modes pinMode(RED_LED_PIN, OUTPUT); pinMode(YELLOW_LED_PIN, OUTPUT); pinMode(GREEN_LED_PIN, OUTPUT); // Starts serial communication at 115200 bps Serial.begin(115200); // Sets the Arduino serial port that will be used for // communication, how long it will take before a status request // times out and how often status requests should be sent to // BitVoicer Server. bvsp.begin(Serial, STATUS_REQUEST_TIMEOUT, STATUS_REQUEST_INTERVAL); // Defines the function that will handle the frameReceived // event bvsp.frameReceived = BVSP_frameReceived; // Prepares the BVSMic class timer bvsm.begin(); } void loop() { // Checks if the status request interval has elapsed and if it // has, sends a status request to BitVoicer Server bvsp.keepAlive(); // Checks if there is data available at the serial port buffer // and processes its content according to the specifications // of the BitVoicer Server Protocol bvsp.receive(); // Checks if there is one SRE available. If there is one, // starts recording. if (bvsp.isSREAvailable()) { // If the BVSMic class is not recording, sets up the audio // input and starts recording if (!bvsm.isRecording) { bvsm.setAudioInput(BVSM_AUDIO_INPUT, EXTERNAL); bvsm.startRecording(); } // Checks if the BVSMic class has available samples if (bvsm.available) { // Makes sure the inbound mode is STREAM_MODE before // transmitting the stream if (bvsp.inboundMode == FRAMED_MODE) bvsp.setInboundMode(STREAM_MODE); // Reads the audio samples from the BVSMic class int bytesRead = bvsm.read(audioBuffer, AUDIO_BUFFER_SIZE); // Sends the audio stream to BitVoicer Server bvsp.sendStream(audioBuffer, bytesRead); } } else { // No SRE is available. If the BVSMic class is recording, // stops it. if (bvsm.isRecording) bvsm.stopRecording(); } } // Handles the frameReceived event void BVSP_frameReceived(byte dataType, int payloadSize) { // Checks if the received frame contains binary data // 0x07 = Binary data (byte array) if (dataType == DATA_TYPE_BINARY) { // If 2 bytes were received, process the command if (bvsp.getReceivedBytes(receiveBuffer, RECEIVE_BUFFER_SIZE) == RECEIVE_BUFFER_SIZE) { analogWrite(receiveBuffer[0], receiveBuffer[1]); } } } Este bosquejo tiene cuatro partes principales:
- Referencias de la biblioteca y declaración de variables: las dos primeras líneas incluyen referencias a las bibliotecas BVSP y BVSMic . Estas bibliotecas son proporcionadas por BitSophia y pueden encontrarse en la carpeta de instalación de servidor BitVoicer. Las otras líneas declaran constantes y variables utilizadas en el dibujo. La clase BVSP se utiliza para comunicarse con el servidor de BitVoicer y la clase BVSMic se utiliza para capturar y almacenar muestras de audio.
- Configuración de función: esta función inicializa la comunicación serial, la clase de la BVSP, la clase de BVSMic y establece el "controlador de eventos" (es en realidad un puntero a función) para el evento frameReceived.
- Lazo función: esta función realiza tres acciones importantes: solicita información de estado al servidor (función keepAlive()), comprueba si el servidor ha enviado todos los datos y procesa los datos recibidos (receive() función) y controla la grabación y envío de flujos de audio (funciones isSREAvailable(), startRecording(), stopRecording() y sendStream());
- Función BVSP_frameReceived: esta función es llamada cada vez que la función receive() identifica que un marco de completa ha sido recibida. Aquí corro el comando enviado desde el servidor de BitVoicer. El comando contiene 2 bytes. El primer byte indica el pin y el segundo byte indica el valor del pin. Utilizar la función analogWrite() para establecer el valor apropiado en el pasador.

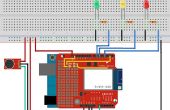
![Arduino voz / reconocimiento de voz con el módulo de Geeetech [Tutorial] Arduino voz / reconocimiento de voz con el módulo de Geeetech [Tutorial]](https://foto.askix.com/thumb/170x110/4/df/4df7db768df778afe854216d5d48b13d.jpg)